Flutter Layout Basics - Stack Layout#
Stack layout is suitable for situations where child views are stacked together, and their positions can be determined relative to the boundaries of the parent view.
For example, it can be used to add text over an image, or to add gradient shadows over a button, etc.
The Stack Widget's child views can either be positioned or non-positioned. Positioned child views refer to those wrapped in a Positioned widget, which confirm their position by setting the top, bottom, left, and right properties relative to the Stack, with at least one of them being non-null.
The size of the Stack Widget depends on all non-positioned child views. The position of non-positioned child views is determined by the alignment property (when alignment is left-to-right, child views start from the top left corner; when alignment is right-to-left, child views start from the top right corner).
Basic Usage of Stack#
Common Properties of Stack#
- Common properties of Stack
- children: Child views
- alignment: Alignment of child views
- topLeft: Top left aligned
- topCenter: Top center aligned
- topRight: Top right aligned
- centerLeft: Center left aligned
- center: Center aligned
- centerRight: Center right aligned
- bottomLeft: Bottom left aligned
- bottomCenter: Bottom center aligned
- bottomRight: Bottom right aligned
- clipBehavior, clipping, which may affect performance
- Clip.hardEdge: This option is the default for Stack
- Clip.antiAlias: Smooth clipping
- Clip.antiAliasWithSaveLayer
- Clip.none: No clipping needed
- fit: Child view filling method
- StackFit.loose: Uses the size of child components
- StackFit.expand: Fills the area of the parent view
- StackFit.passthrough: Pass-through, uses the layout method of the Stack's parent view
- textDirection
- TextDirection.ltr
- TextDirection.rtl
Common properties of Positioned are as follows:
- Common properties of Positioned
- child
- height
- width
- bottom
- left
- right
- top
Alignment#
The code is as follows:
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
var stack = new Stack(
alignment: Alignment.bottomRight,
children: [
new Container(
width: 300.0,
height: 300.0,
color: Colors.orange,
),
new Container(
width: 200.0,
height: 200.0,
color: Colors.green,
),
new Text(
'alignment bottomRight',
style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white, fontSize: 21),
)
],
);
return MaterialApp(
title: 'StackView Widget',
home: Scaffold(
appBar: new AppBar(
title: new Text('StackView Widget'),
),
body: Center(
child: stack,
),
),
);
}
}
The effect is as follows:
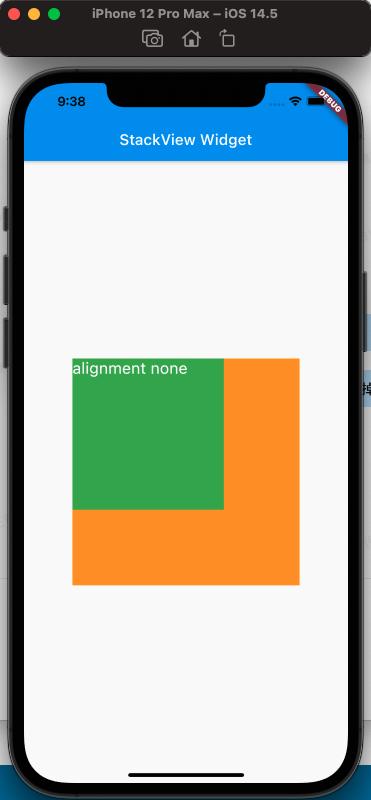
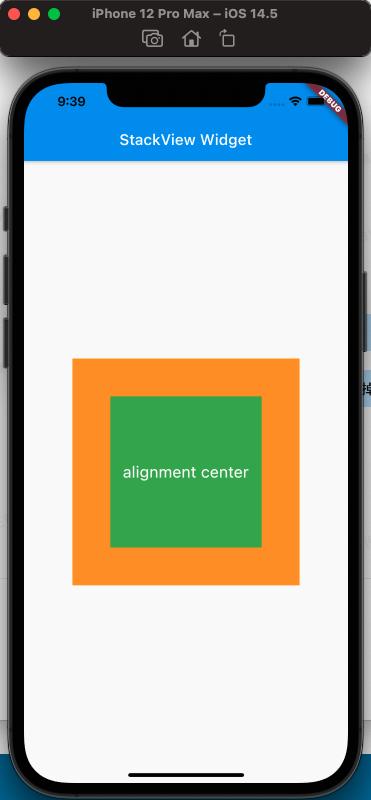
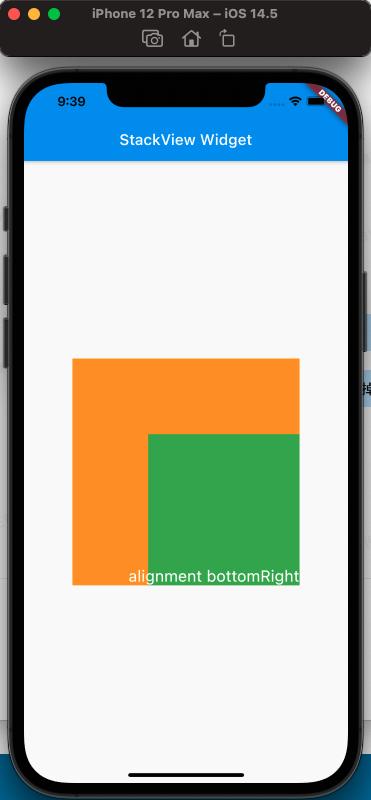
From the comparison above, it can be seen that the alignment property affects the arrangement of the Stack's child views.
clipBehavior Property#
To conveniently observe the effect of clipBehavior, we need to write a child view that exceeds the Stack using the Positioned Widget, setting top and left to negative values.
The code is as follows:
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
var stack = new Stack(
clipBehavior: Clip.antiAliasWithSaveLayer,
children: [
new Container(
width: 300.0,
height: 300.0,
color: Colors.orange,
),
Positioned(
child: new Container(
width: 200.0,
height: 200.0,
color: Colors.green,
),
left: -20,
top: -20),
new Text(
'clip antiAliasWithSaveLayer',
style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white, fontSize: 21),
),
],
);
return MaterialApp(
title: 'StackView Widget',
home: Scaffold(
appBar: new AppBar(
title: new Text('StackView Widget'),
),
body: Center(
child: stack,
),
),
);
}
}
The effect is as follows:
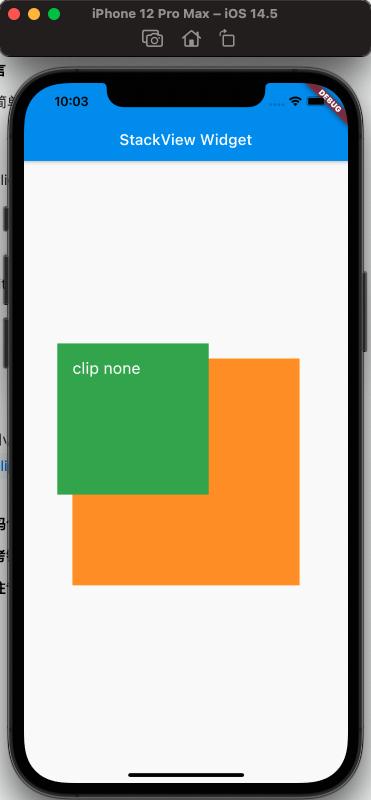
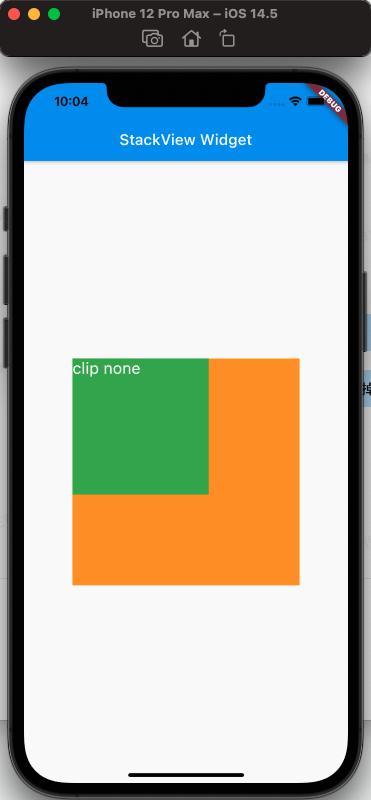
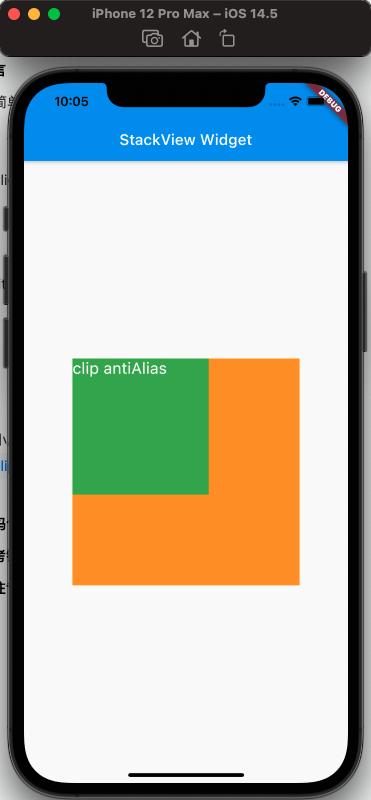
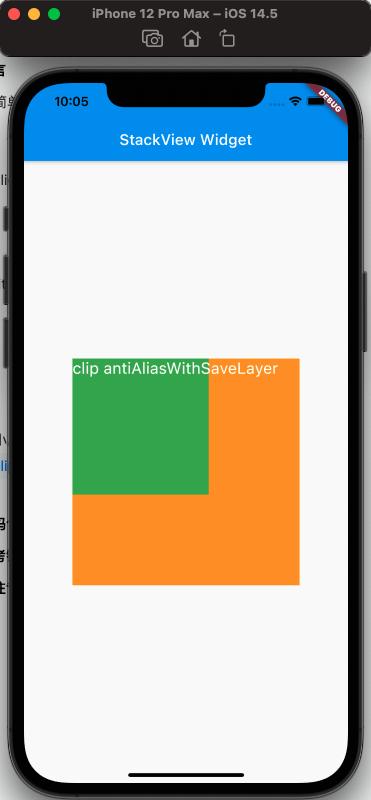
From the above, the effect of clipBehavior can be seen.
fit Property#
The filling method of fit, the expand and loose properties of fit are easy to distinguish, but the difference between loose and passthrough properties needs special attention. To easily distinguish the differences, here we use Row as the parent view of Stack.
Simply put, expand fills the parent view; loose follows the size of the child view; passthrough follows the constraints of the parent view's parent view.
The code is as follows:
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
var stack = new Stack(
// alignment: Alignment.bottomRight,
fit: StackFit.passthrough,
children: [
new Container(
width: 300.0,
height: 300.0,
color: Colors.orange,
),
new Container(
width: 200.0,
height: 200.0,
color: Colors.green,
),
new Text(
'StackFit passthrough',
style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white, fontSize: 21),
),
],
);
return MaterialApp(
title: 'StackView Widget',
home: Scaffold(
appBar: new AppBar(
title: new Text('StackView Widget'),
),
body: Center(
child: Row(
children: [Expanded(child: stack)],
),
),
),
);
}
}
The effect is as follows:
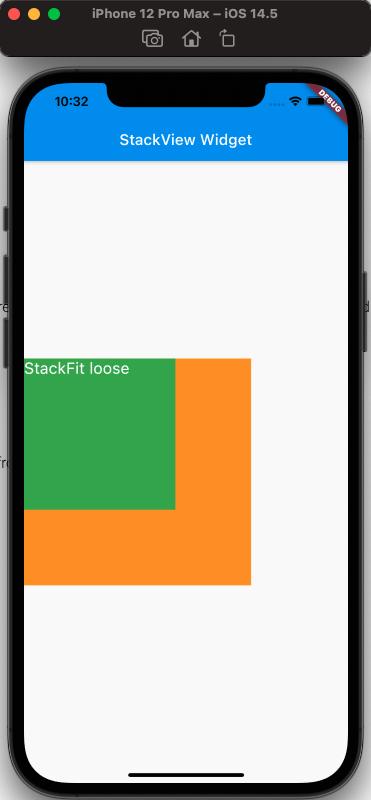

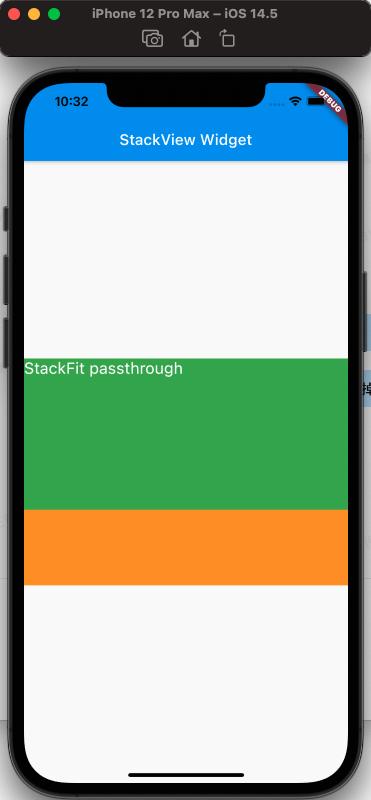
From the above, it can be seen that when StackFit is passthrough, it uses the Row's Expanded layout; when StackFit is loose, it uses the layout of the child view; when StackFit is expand, it uses the layout of the Stack.
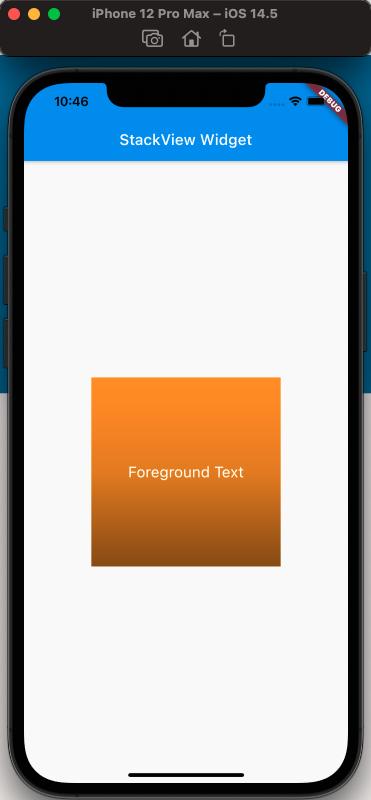
Using Stack to Achieve Gradient Background Effect#
The code is as follows:
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
var stack = SizedBox(
width: 250,
height: 250,
child: Stack(
children: [
Container(
width: 250,
height: 250,
color: Colors.orange,
),
Container(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(5.0),
alignment: Alignment.center,
decoration: BoxDecoration(
gradient: LinearGradient(
colors: [
Colors.black.withAlpha(0),
Colors.black12,
Colors.black45,
],
begin: Alignment.topCenter,
end: Alignment.bottomCenter,
)),
child: const Text('Foreground Text',
style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white, fontSize: 20.0))),
],
),
);
return MaterialApp(
title: 'StackView Widget',
home: Scaffold(
appBar: new AppBar(
title: new Text('StackView Widget'),
),
body: Center(
child: stack,
),
),
);
}
}
The effect is as follows:
References#
Stack Dev Doc
Positioned Dev Doc
StackFit Dev Doc
Flutter Free Video Season 3 - Layout